Security is not just a defense mechanism, but it is a matter of trust and dependence.
The new competitive age of digitization is seeking more attention due to the increasing rate of cyber threats. It is highly essential to safeguard the hardware devices before the software systems as the black hat hit rate is equally threatening to both software and hardware devices and take the calculated steps to bring up the digital mutiny.
In this perspective, let us shed some light on what happens if hardware security is ignored.
- Manipulations are carried on the system’s input and output functions
- Sensitive data is vulnerable to malware attack
- Software security is not enough ensured against cyber attacks
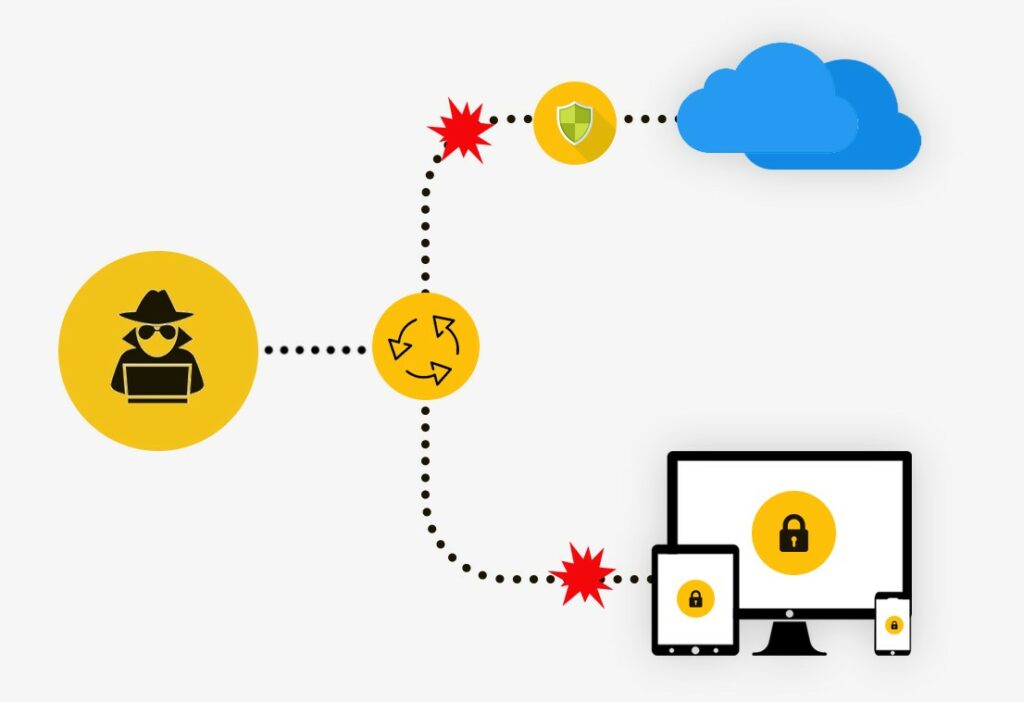
Sometimes we cannot even imagine the amount of loss incurred when a proper hardware security system is not installed. So, it’s high time that we start focusing on securing our Hardware as equally as we concentrate on software security.
What is hardware security?
Cryptographic Engineering is the baseline cause for the origin of the term Hardware Security. Ensuring the physical security which cannot be easily obtained by the software is the main reason for focus here. But, when it comes to a professional definition, securing over-all physical attributes like design, keystrokes, access controls, speed, power consumption, supply chain management together with crypto processing is called as Hardware security.
The entire securing process can be attained by using a physical HSM (Hardware Security Module), which is either plugged in or attached to the computer systems. The HSM performs the entire cryptography life cycle process, which includes provisioning, managing, storing, and disposing mechanisms. Some listed features of using the HSM’s are:
- Provides high alert security
- Encryption and Decryption procedures
- Digital signature protection
- Message Authentication codes
- Keystroke management
- Verifies the data integrity
- Accelerates the SSL connections and smart key generation
Types of Hardware Security Modules and their Applications:
The HSM’s are internationally certified modules that promise to provide unbreakable security walls and also validated successfully with FIPS 140 Security Level4 security standard. Such HSM’s are aiding the digital security systems with the following applications
#1. CA HSM
The Certification Authority (CA) HSM is widely used in the Public Key Interface environment to manage the entire asymmetric keystrokes and sensitive data. It helps in protecting the logical information with specific security measures and also performs the auditing of logs. Even the keystroke information is also bagged with a strong backup.
Applications: Networking Systems, Industries, General systems, E-Platforms, etc.
#2. Bank HSM
A unique and specially designed HSM’s are used in all the payment systems nowadays. These are designed to support all the banking or other financial transactions with highly defined security terms. They help in verifying the user identity to validate the entered PIN each time. Encryption mechanism is also carried out in the entire transaction process with enhanced secure key management.
Applications: Banks Systems, Financial Organizations, Online Payments, Money Transfers, etc.
#3. DNS SEC
This HSM manages the Zone file signatures and handles the sensitive information.
Applications: Digital Signatures, Confidential Information Gathering, Security Agencies, etc.
#4. Cryptocurrency wallet
The HSM aims to bestow the guaranteed cryptocurrency transactions by storing and managing both the public and private keys.
Applications: Bitcoin, Ethereum, Dogecoin, etc.
#5. Establishing an SSL connection
The concerned HSM engineers the performance of HTTPS protocols and increases the speed of SSL connection by eradicating the unwanted RSA operations. Also, Keystroke management is handled in this type of HSM.
Applications: All HTTPS protocols.
Importance of Maintaining Hardware Security
Proper maintenance of hardware security is a much-needed concern and should be taken on a serious note to break down the speed of physical cyber-attacks. Any weakness, either in keystroke or other related physical devices such as routers, CPU’s, etc., can attract and invite the multiple attacking modes to invade.
For example, let us consider a Side-Channel attack and Power Glitch attack, which directly conveys a message stating what happens when we ignore hardware security.
Side-Channel Attack:
This attack mainly concentrates on the technical information of the system’s internal structure and then starts to implant the violations in it. The gathered information includes the System Timing, Keystrokes, Power consumption, electro-magnetic leaks, and sound system. The side-channel attack has different forms of attacking modes and can be triggered at any point in time once the system’s information is stolen. The listed ones are:
- Power-Monitoring Attack
- Timing Attack
- Cache Attack
- Electro-Magnetic Attack
- Sensitive Data Theft
Glitch Attack:
A glitch can be defined as a suspicious attack on the performance of any device. Targeting the consumption features of the device and altering it with the malware inputs, which results in the machine break down, is referred to as being a glitch attack. Manipulating the device power, time, and memory inputs are the main motto of the attacker here.
- Clock Glitch attack
- Power Glitch attack
Conclusion:
Hence, hardware security must be given the top priority to ensure highly secured transactions or communications in the present digital environment. The easiest tip to tackle hardware security is to use the most suitable and effective HSM without fail.
